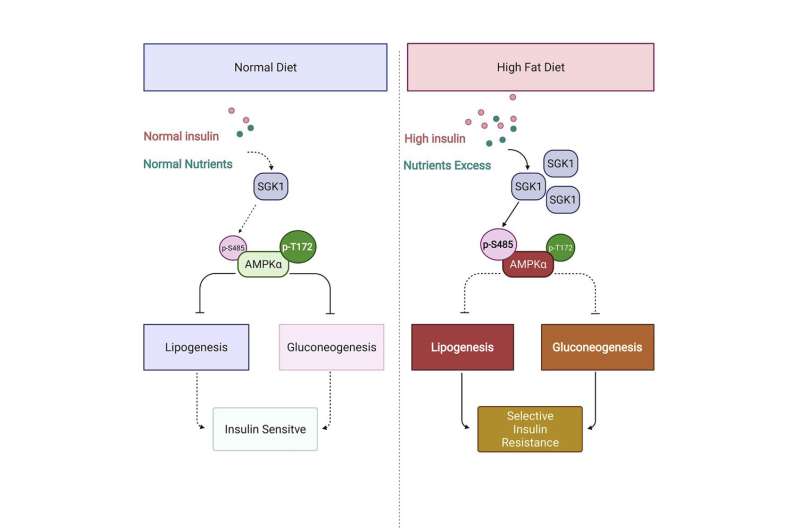
A central feature of type 2 diabetes is an inability of the body’s cells to respond to insulin, a hormone that keeps blood glucose levels normal. Critical to this balance is the liver, which both stores and manufactures glucose depending on the body’s need. New research published in Cell Reports that was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) indicates that an enzyme called serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase (SGK) drives insulin resistance in the liver and therefore may represent a promising therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes.
“We decided to study the role of SGK in insulin action and metabolism because the field has assumed, since it looks very similar to another insulin-activated kinase called Akt, that SGK would do the same thing as Akt,” says senior author Alexander A. Soukas, MD, Ph.D., a principal investigator in MGH’s Center for Genomic Medicine and Diabetes Unit and an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. “We had the idea, based upon some early experiments, that it might actually be working in opposition to Akt, and that it might represent a way to target insulin resistance in diabetes in a very different way, promoting metabolic health and insulin sensitivity.”
Indeed, the team’s experiments revealed that when mice ate an unhealthy diet, Sgk (the mouse version of SGK) hindered the action of insulin by inhibiting the beneficial metabolic effects of a liver molecule called AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Blocking Sgk activity released the brakes on AMPK, causing the liver to be more sensitive to insulin and to burn fat in the process. “In this way, targeting Sgk may be a way to target metabolic changes in type 2 diabetes in a way not previously thought possible,” says Soukas.
Source: Read Full Article
