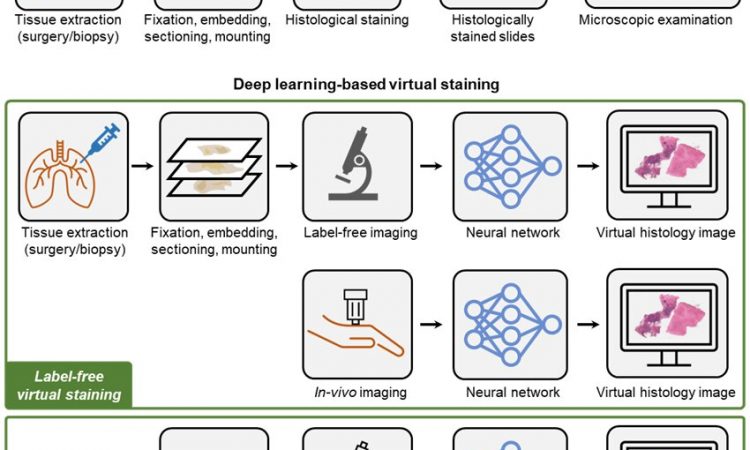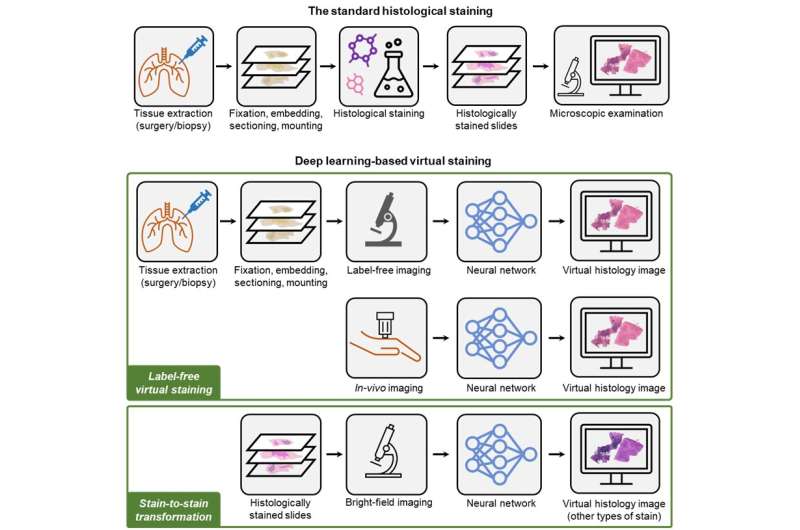
Histological staining, a principal tool for tissue examination in clinics and life-science research, has been routinely carried out in pathology laboratories to assist in assessing pathophysiology and disease diagnostics. Despite its widespread use, standard histological staining procedures are plagued with drawbacks such as labor-intensive preparation steps, lengthy turnaround time, high costs, and inconsistent outcomes.
Virtual staining, a deep learning-based method to digitally generate histological stains, has the potential to revolutionize traditional histological staining workflows. By eliminating the need for chemical staining and toxic compounds, virtual staining provides a rapid, cost-effective, and accurate alternative to traditional staining methods, which can potentially improve the accuracy and speed of diagnoses, leading to better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
The Ozcan group at UCLA has recently published a Review paper on this emerging virtual staining technology. Titled “Deep Learning-enabled Virtual Histological Staining of Biological Samples,” this Review paper provides a comprehensive overview of recent advances in the virtual staining field. It covers the basic concepts, the typical development workflow, and the future perspectives of deep learning-enabled virtual staining technology. It also highlights some key results from representative works, summarizing the up-to-date research progress in this rapidly evolving field.
Published in Light: Science & Applications, a journal of the Springer Nature, this Review paper on virtual staining provides a valuable resource for scholars, optical engineers, microscopists, computer scientists, biologists, histologists, and pathologists alike. “We believe this Review paper will serve as an atlas of the technical developments in this research area, providing a top-level understanding of the latest advancements in virtual staining,” said Dr. Aydogan Ozcan, “and we hope it will inspire readers from diverse scientific fields to further expand the scope and applications of this exciting field and continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with virtual staining”.
More information:
Bijie Bai et al, Deep learning-enabled virtual histological staining of biological samples, Light: Science & Applications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41377-023-01104-7
Journal information:
Light: Science & Applications
Source: Read Full Article