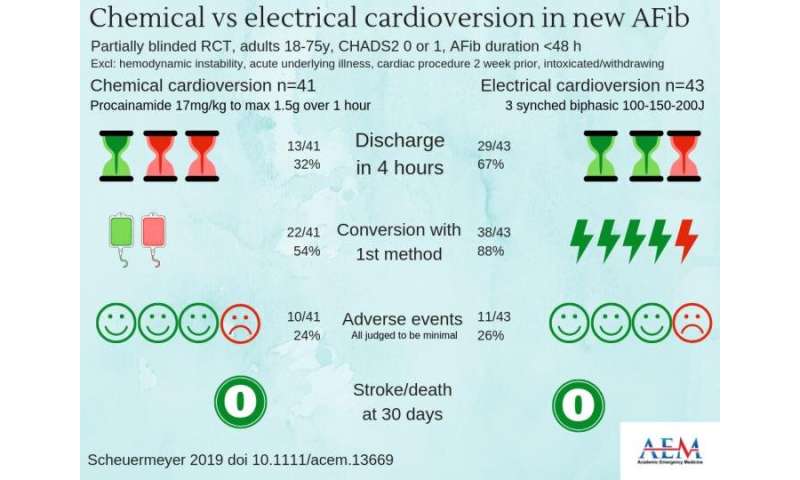
A multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial confirms that both chemical-first and electrical-first approaches are effective strategies for acute atrial fibrillation; however, an electrical-first strategy results in a significantly shorter emergency department (ED) length of stay. The study findings are published in the September 2019 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
The lead author of the study is Frank X. Scheuermeyer, MD, MHSc, program head, clinical associate professor, and director of research in the Department of Emergency Medicine at St. Paul’s Hospital and the University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
The trial results showed that in uncomplicated ED atrial fibrillation patients of less than 48 hours, a significantly greater proportion of ED patients were discharged from the ED within four hours when managed with an electrical-first cardioversion strategy, compared to a chemical-first cardioversion strategy. In addition, the median LOS was shorter by 1.2 hours for the electrical-first group.
The findings add to the literature by comparing two accepted treatments, measuring important outcomes—including patient-reported results—and demonstrating that these patients, irrespective of initial management strategy, are safe; have minimal discomfort after their ED visit; and have an acceptable QoL at 3 and 30 days.
The study may assist clinicians by demonstrating that the electrical-first strategy may restore sinus rhythm more quickly. The results should encourage clinicians to initially consider an electrical-first approach for such patients.
Commenting on the study is Editor-in-Chief of the Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine, Ian G. Stiell, MD, MSc, a distinguished professor and senior scientist in the Department of Emergency Medicine, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, University of Ottawa:
Source: Read Full Article
